The 3Delight Material is a general purpose, physically plausible, material that can be used to render a large variety of surfaces. Its main interesting feature is its ability to simulate surfaces that have a coating. Coated materials include common real world objects such as furniture, cars, toys and many plastics. The coating layer adds interesting effects on gazing angles and adds an additional specular highlight (from the coating itself) that can be observed on most coated materials (it is especially noticeable on car paint and many legacy shaders simulate this effect by having a secondary highlight control, which is not physically plausible).
The 3Delight Material with three group of parameters:
Base Layer, Coating and Subsurface
Coating | ||||
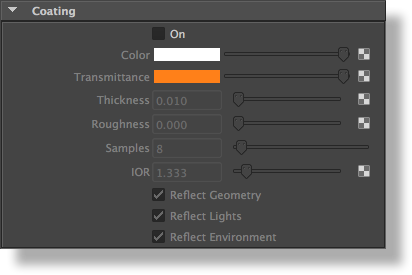
On | Specifies wether or not there is a coating on top of the Base layer. Visually, the presence of coating adds the following two phenomenas to the look of the layer:
| |||
Color | Colour of the coating. This is basically the color of the specular highlight that is seen on the coated surface. | |||
Transmittance | The color of the interior of coating. Light that travels through the coating will be coloured according to transmittance. | |||
Thickness | Thickness of the coating in scene units (world units). For example, when rendering a coated table of 1 meter, a value of 0.001 means a thickness of 1 millimeter. | |||
Roughness | This controls the specular roughness of the coating material. The smaller the value, the smoother is the surface. | |||
Samples | This is the total number of samples to trace in order to sample the scene in the specular direction. The rougher is the material the more samples are needed to avoid undue noise. | |||
IOR | The index of refraction of the coating layer. A value of 1.3 is usual. | |||
Reflect Geometry | Specifies if the coating reflects the Geometries, Lights and Environment respectively. Disabling the reflection of geometries can speedup rendering because no ray-objects intersections are performed. "Reflect Lights" enables or disables specular highlight from point lights. | |||
Base | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Diffuse Color | This diffuse colour of the base material. | |||
Diffuse Roughness | This controls how diffuse is the material. A value closer to one simulate very rough materials such as chalk. A value of 0 renders a standard "lambertian" diffuse. On a more technical note, this paramter controls the roughness of the Oren-Nayer diffuse model. | |||
Reflection Color | Specifies the color of the specular highlight. | |||
Reflection Roughness | This controls the specular roughness of the base layer. The smaller the value, the smoother is the surface. | |||
Reflection Samples | Specifies the total number of samples to trace in order to sample the scene in the specular direction. The rougher is the material the more samples are needed to avoid noise. | |||
IOR | Sets the index of refraction that will be used for reflection. | |||
Reflect Geometry | Specifies if the base coating reflects Geometries, Lights and the Environment respectively. Disabling the reflection of geometries can speedup rendering because no ray-objects intersections are performed. "Reflect Lights" enables or disables specular highlight from point lights. | |||
Anisotropy | Specifies anisotropy "directionality". 0 means no anisotropy. Positive values will increase anisotropy along the anisotropy direction and negative value will increase it along the perpendicular direction. | |||
Anisotropy Direction | Specifies the anisotropy direction in local tangents space. | |||
Refraction Color | The color of the refraction. Setting this color to 0 disables refraction. | |||
Refraction Roughness | Specifies the roughness of the refraction. The smaller the value, the smoother is the surface. Higher values can be used to emulate "ground glass" for example. | |||
Refraction Samples | Total number of refraction samples to trace. The rougher is the refractive material the more samples are needed to avoid noise. | |||
Refraction IOR | Sets the index of refraction in case the base layer is refractive. | |||
| ||||
On | Specifies wether or not the material has subsurface light penetration. | |||
Scattering | The tint of the light that is scattered inside the material. Visually, this means that the light which penetrates the object far away from its exist point will be tinted by this color. For skin, this would be bluish. | |||
Scattering Scale | Scattering isn't usually confined to the 0..1 range (physically, it is expressed in 1/mm). So to have a use friendly UI in which the scattering can still be expressed as a color, we added a separate scale to control the general amplitude. | |||
Transmittance | Visually, this specifies the color of the light that is diffused nearby the entry point of a light beam. For skin, this would be reddish. | |||
Transmittance Scale | Same as for Scattring Scale but applies for Transmittance. | |||
IOR | The index of refraction of the based layer. | |||
Scale | A global scale that applies to this material. Larger scales will make the object appear more translucent. This is the best way to control how much diffusion goes into the surface. A scale closer to 0 will tend to disable the subsurface scattering effect and the surface will look solid.
| |||
Group | This allows many objects, with different materials, share the same "subsurface simulation". For example, two intersecting cubes with different material properties but with the same group name will have correct subsurface intersecting along the intersecting lines. |