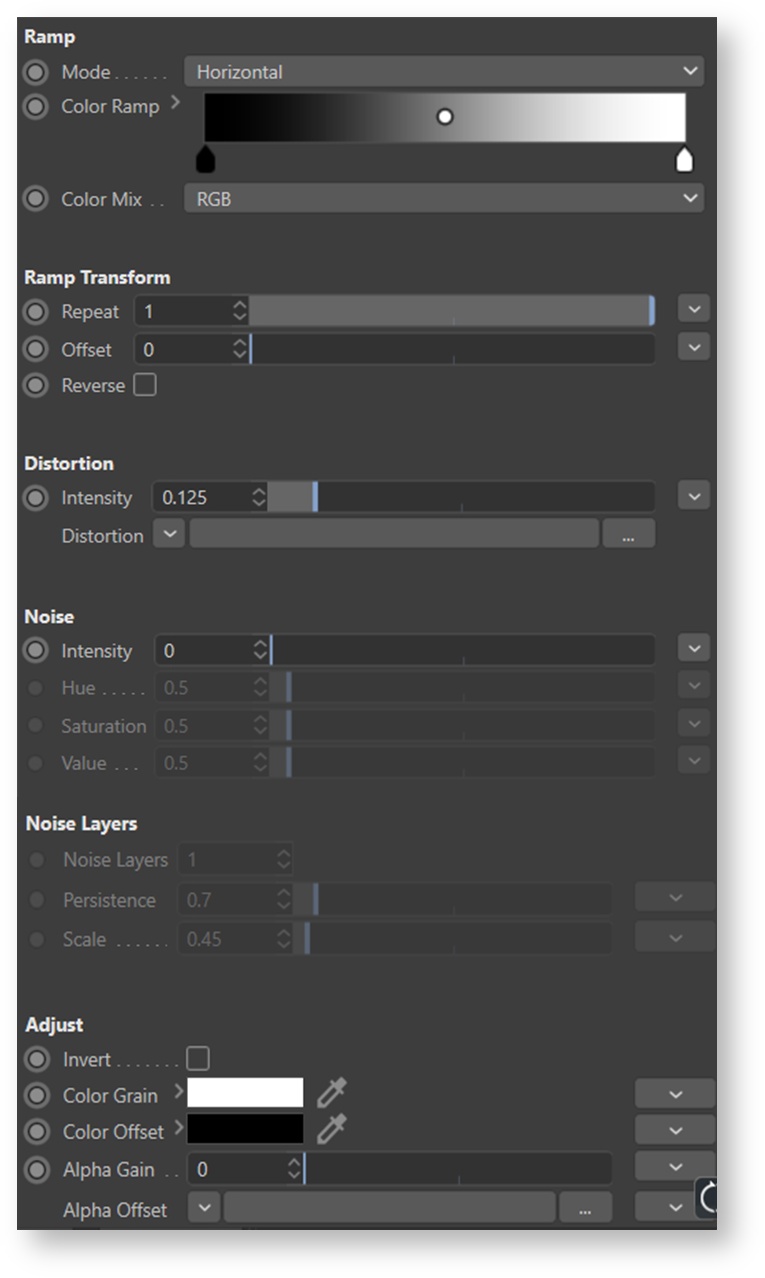
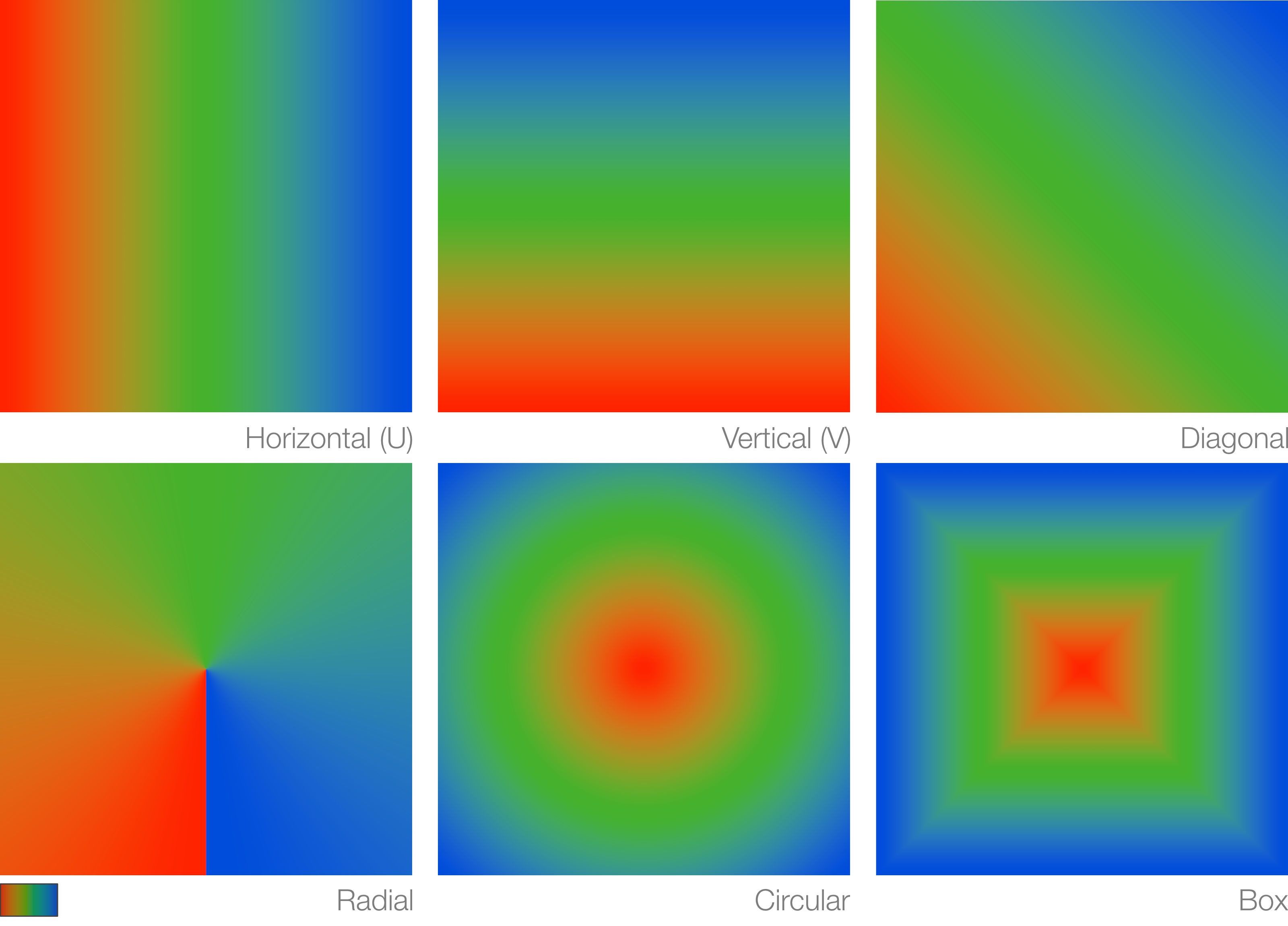
Mode
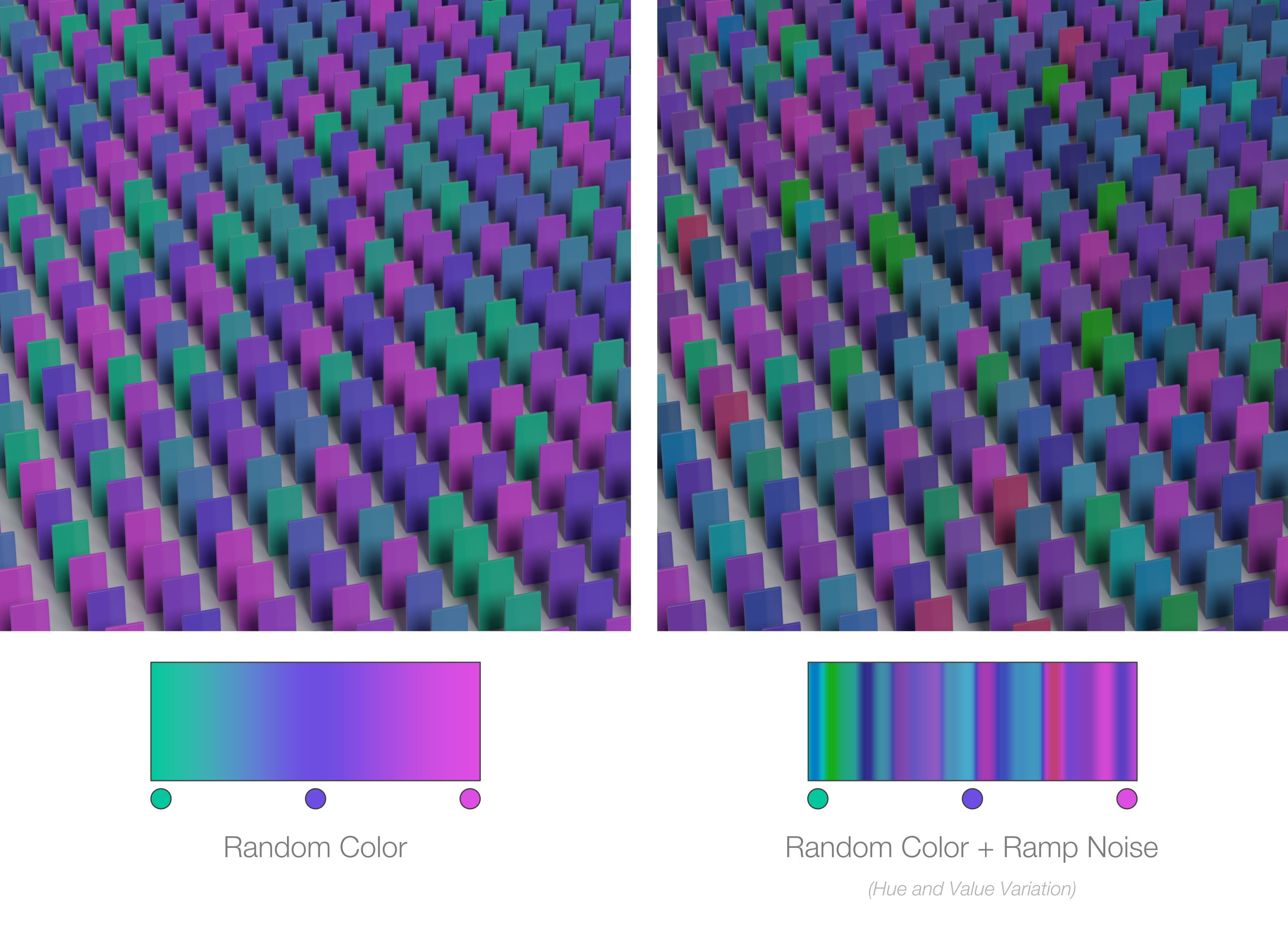
Random Color Mode
This allows to use the ramp as a possible set of random colors to assign to geometry. Each object will receive a single color from the ramp. More variety of colors can be obtained by using with the noise variation.
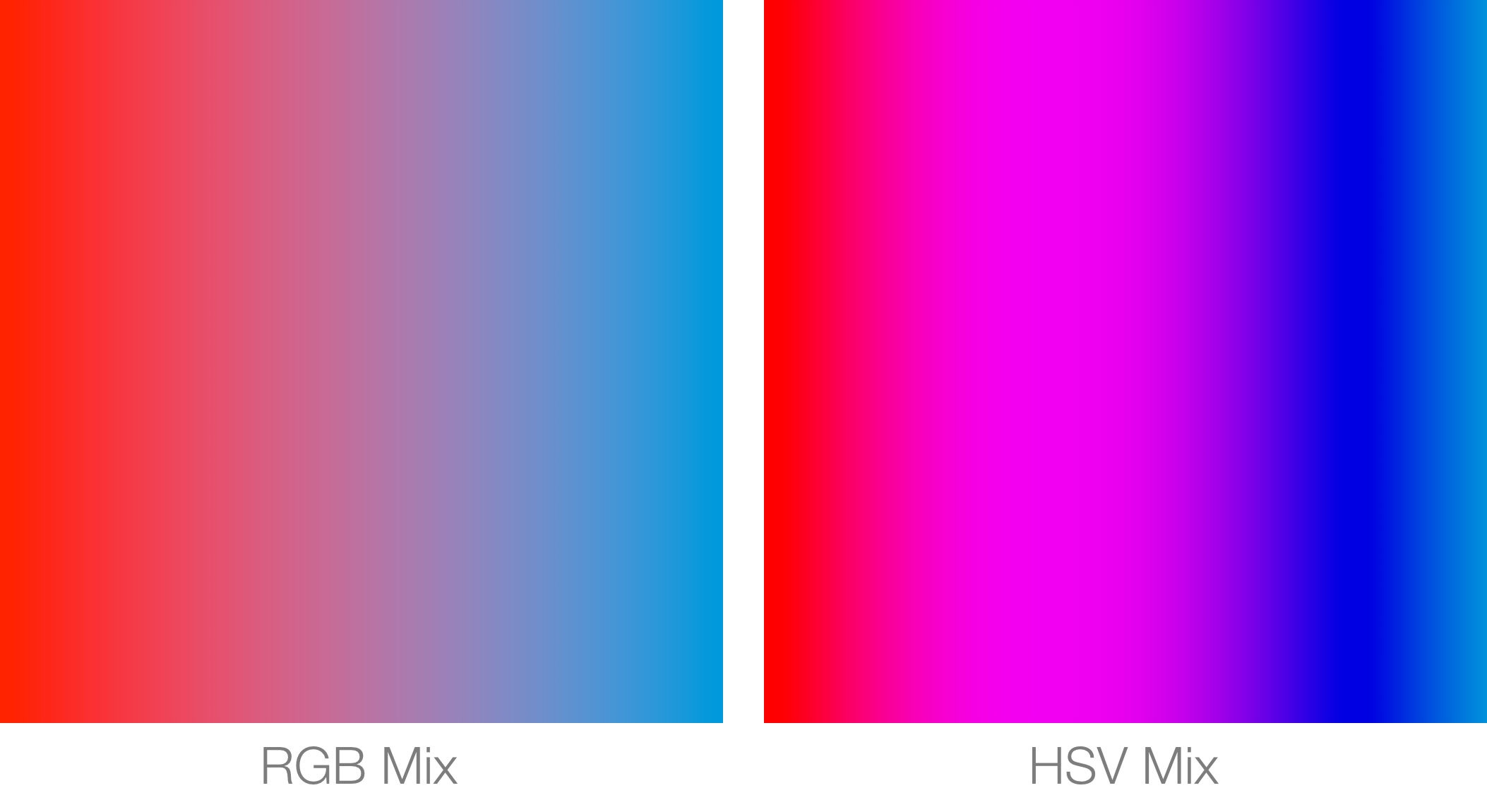
Color Mix
Sets the mixing mode type: either RGB or HSV. Using HSV will generally produce more saturated colors.
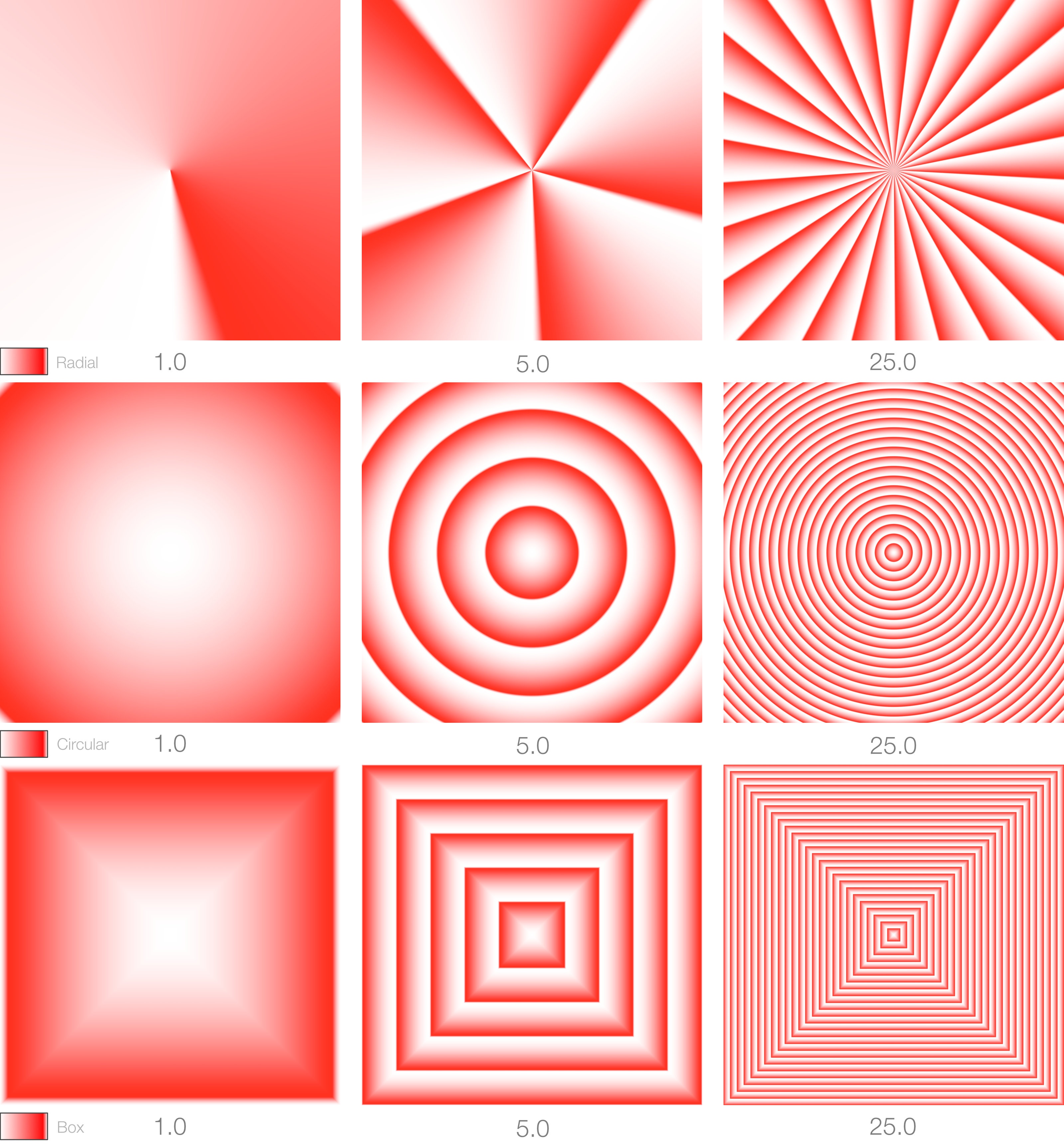
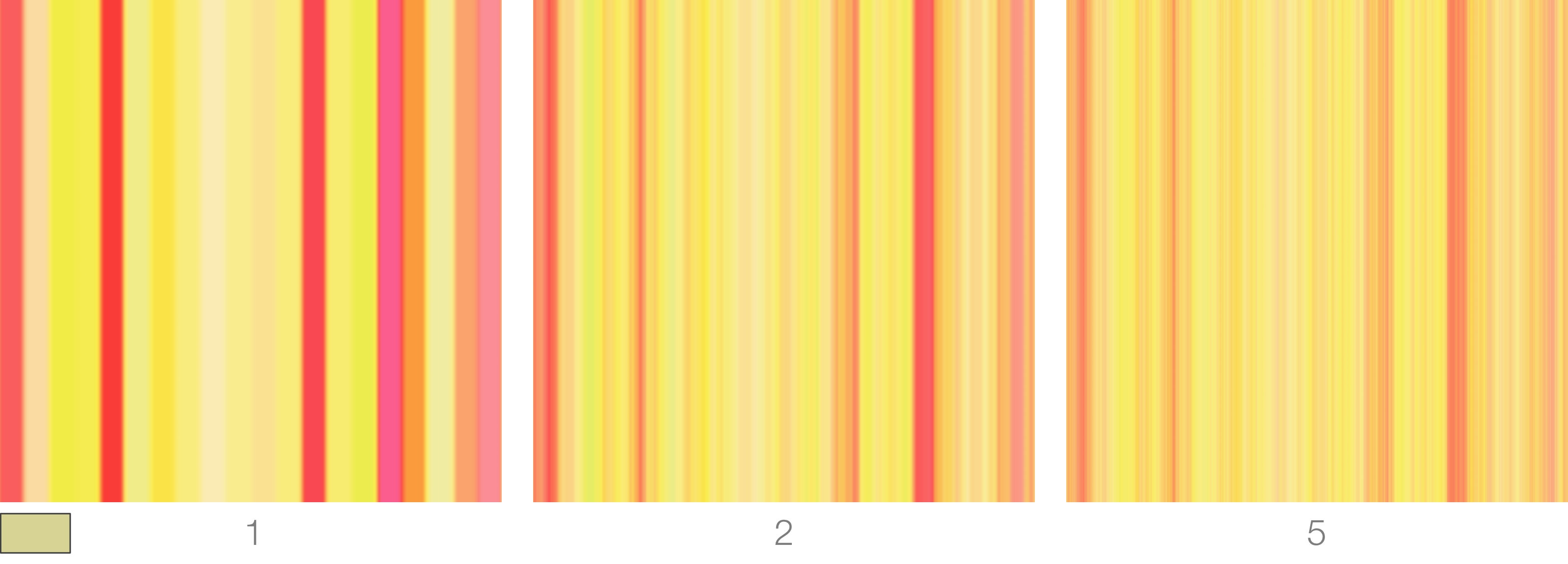
Repeat
Sets how many times each pattern is repeated. Note that 3Delight's ramp repeat is not merely a repeat of UV space: it is unique to each pattern.
Offset
Adds an offset when performing the lookup in the ramp.
Reverse
Reverse ramp's output.
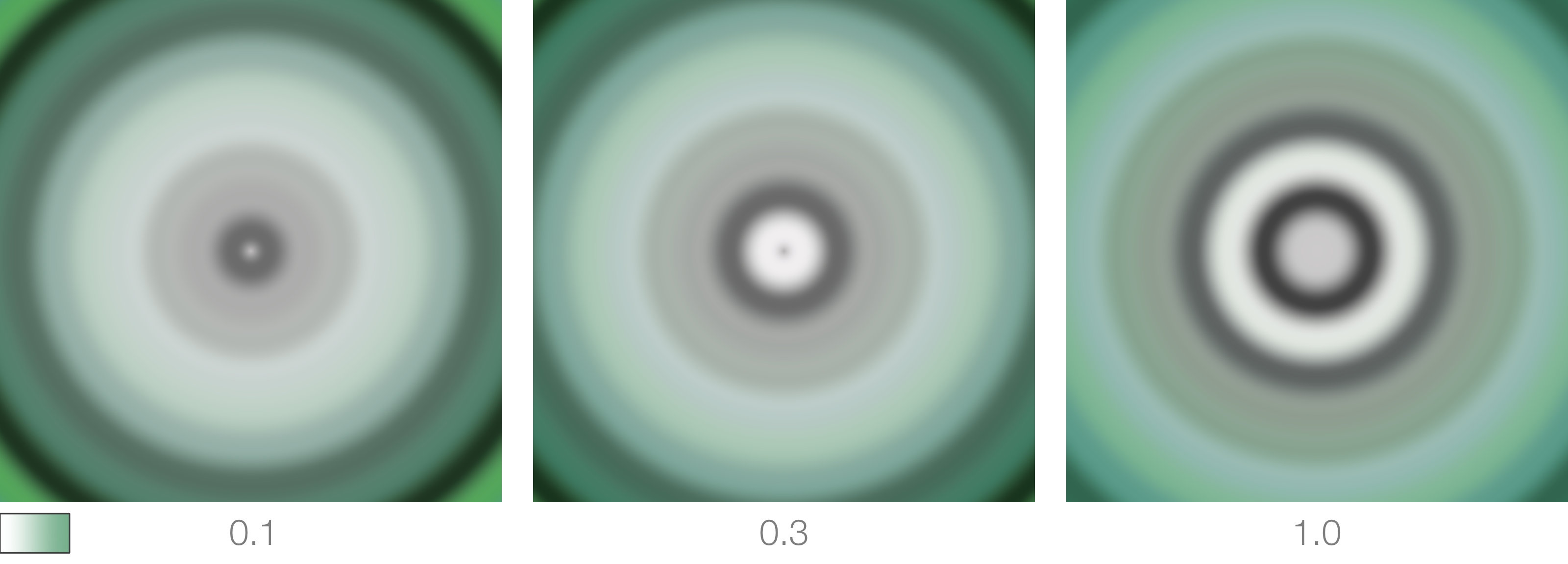
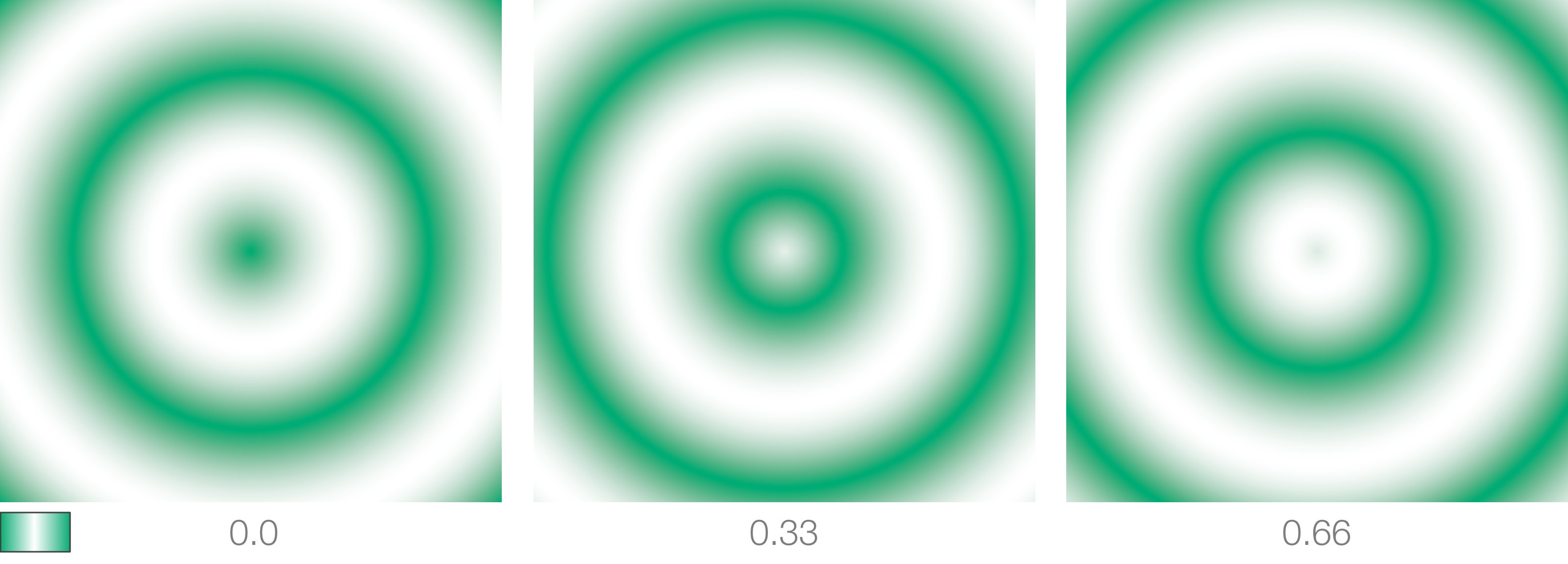
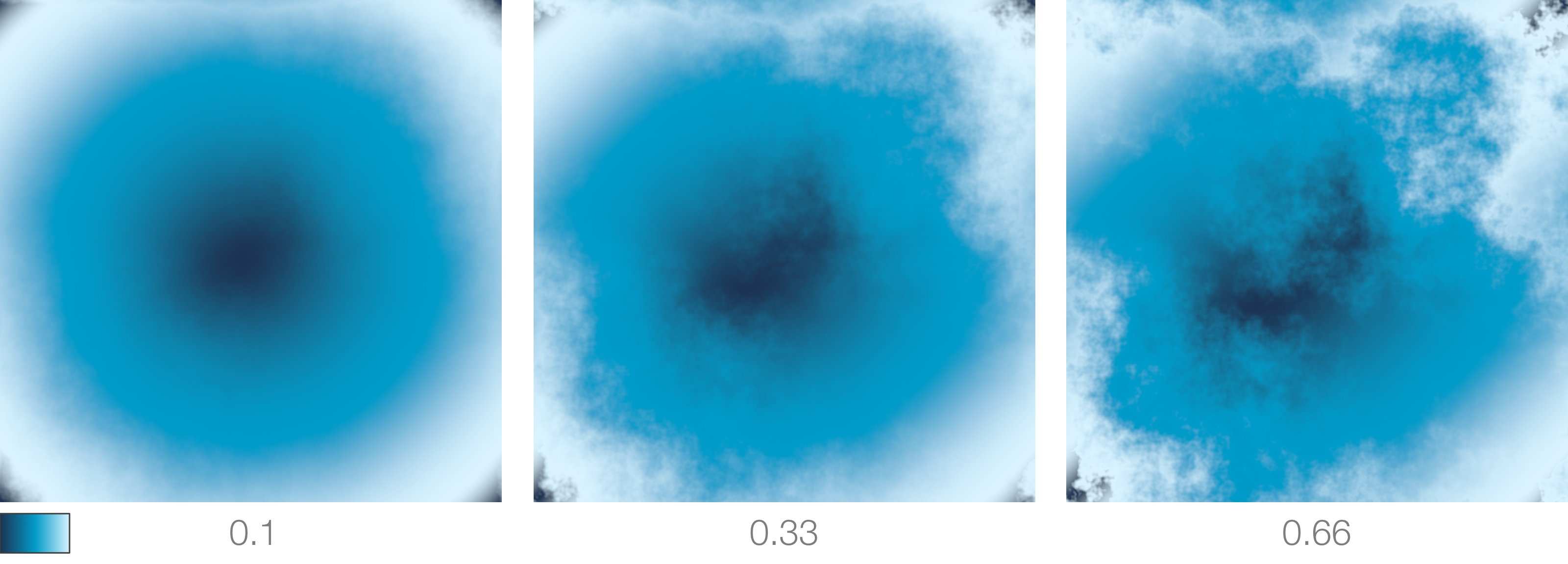
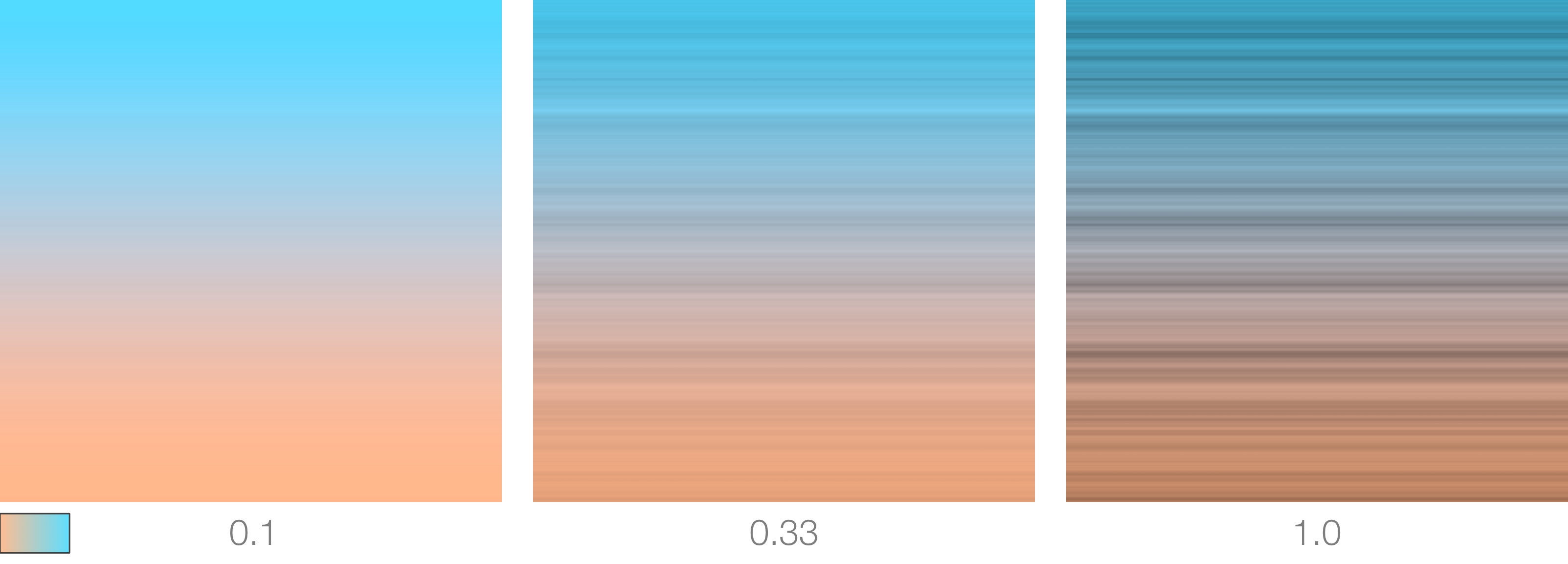
Distortion
Used to apply a distortion to ramp's output. Common usage is to use a procedural noise generator to drive this parameter as shown in the images below.
Distortion Intensity
Sets the strength of the distortion.
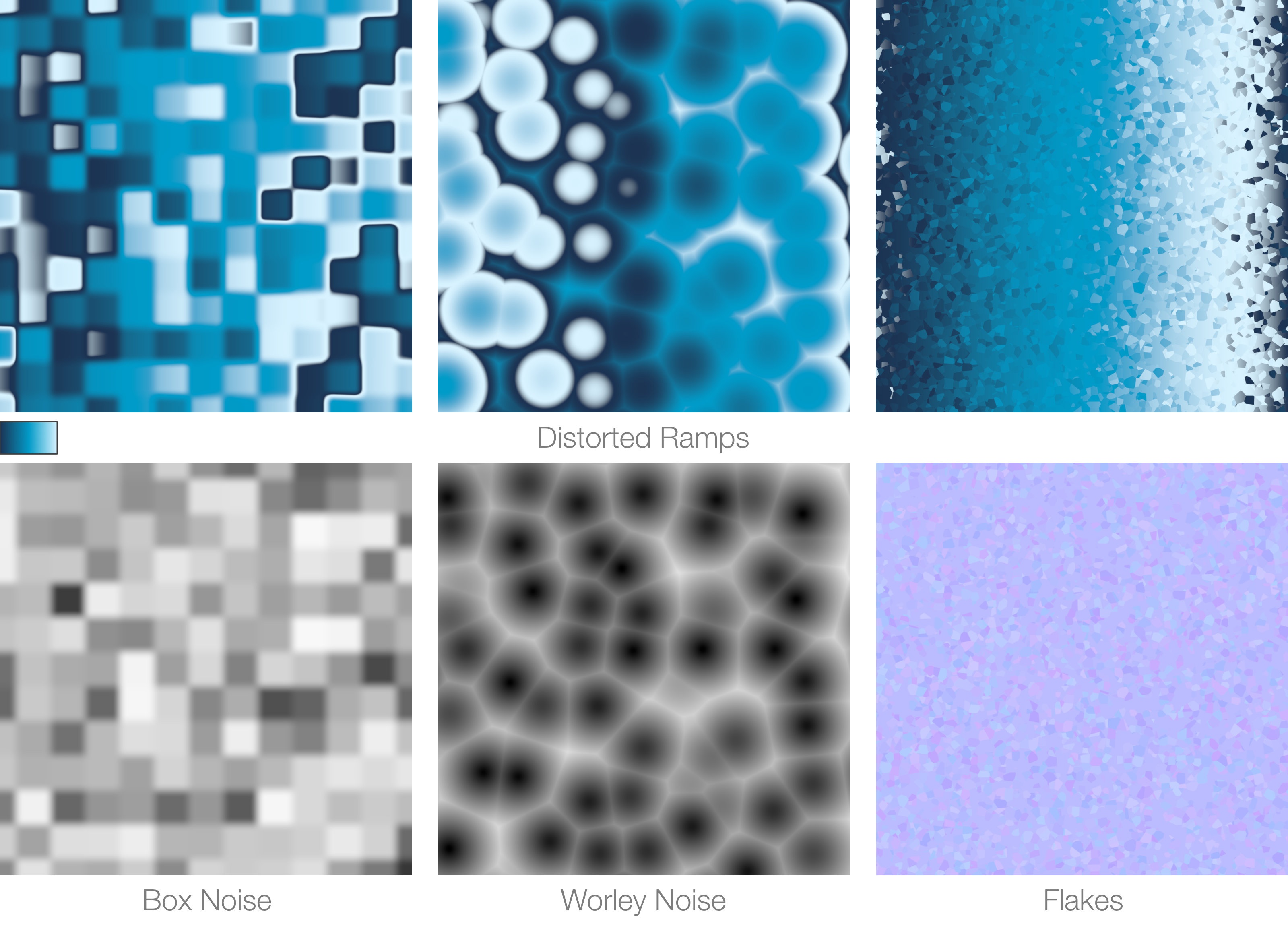
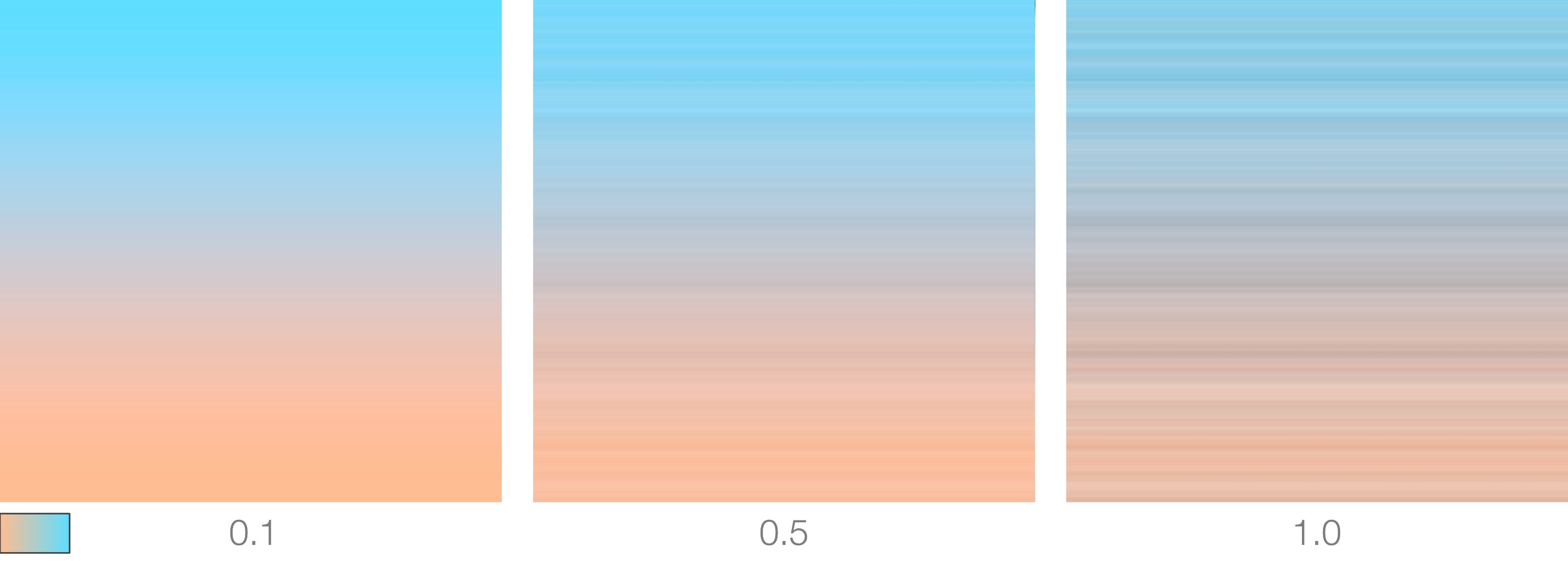
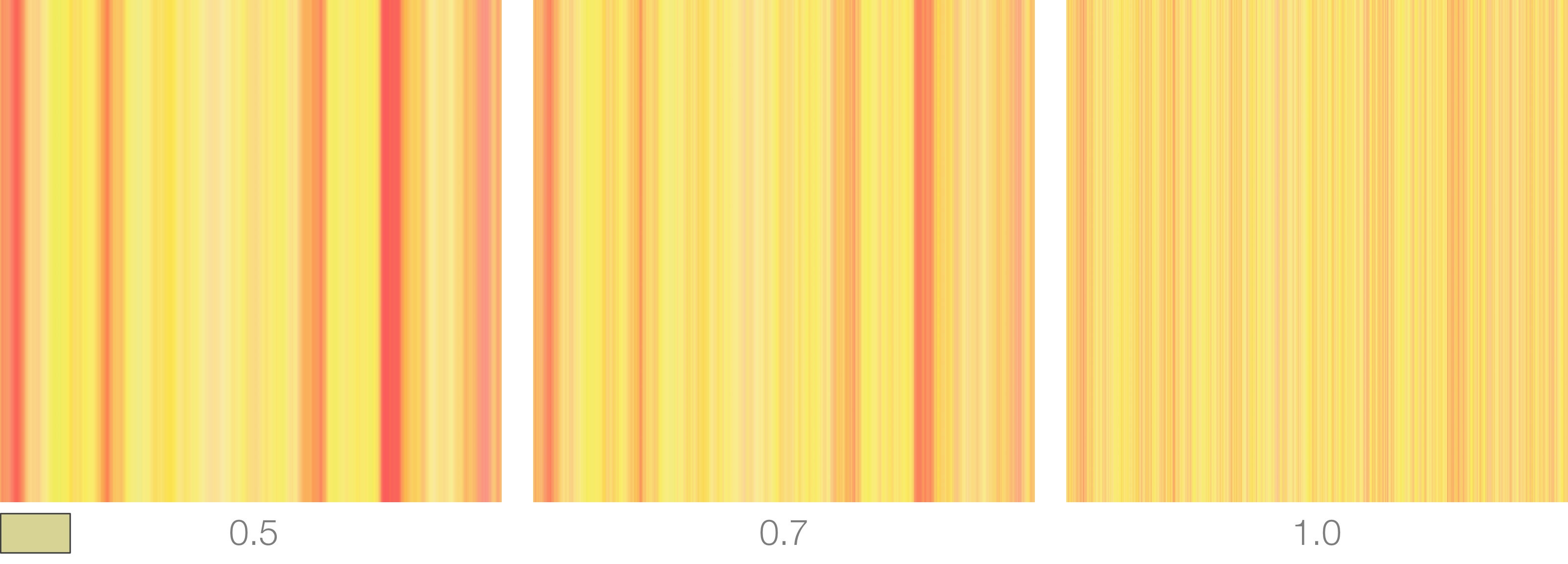
Noise Intensity
A noise pattern can be added to ramp's colors and this parameter controls its global intensity.
Hue Noise Intensity
Applies a perturbation to the hue component of the ramp output. This value is multiplied by Noise Intensity.
Saturation Noise Intensity
Applies a perturbation to the saturation component of the ramp output. This value is multiplied by Noise Intensity.
Value Noise Intensity
Applies a perturbation to the value component of the ramp output. This value is multiplied by Noise Intensity.
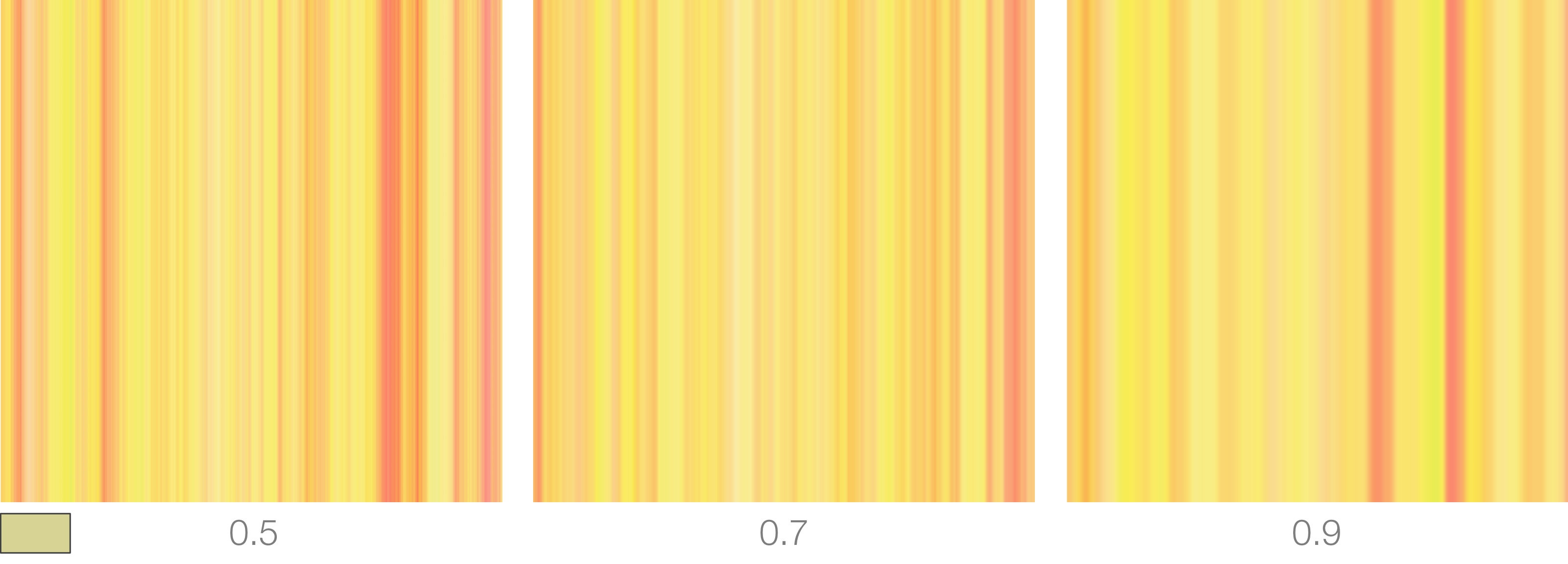
Noise Scale
Sets the general scale of the noise. Smaller scale produce finer details.
Noise Offset
Adds an offset to the resulting noise. This is useful to generate different noise patterns.
Noise Stepping
Allows for sharper edges in the perturbation created by the noise. A value of 1 will produce sharp bands.
Noise Time
The time of the noise is generally used to have a consistently animated noise pattern from frame to frame. It can also be used to select a different pattern.
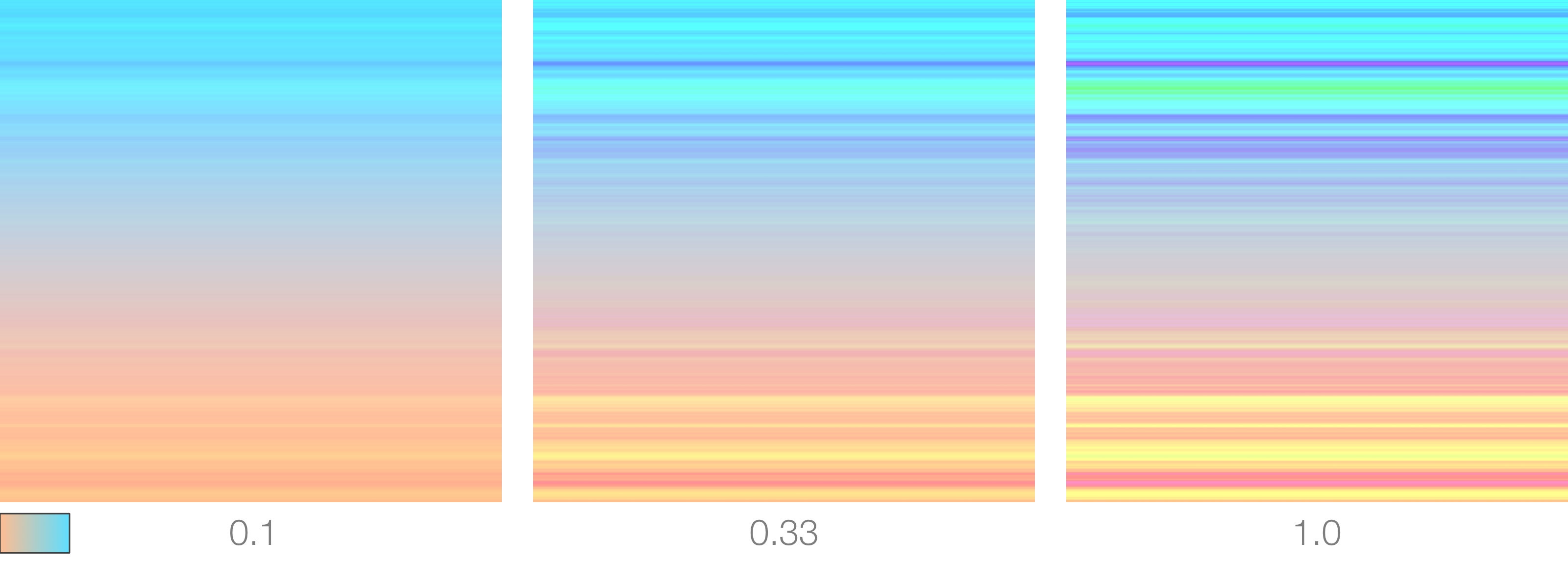
Noise Layers
How many noie layers to combine together. This is commonly called fractal noise. The more layers you add, the more details will appear in the noise pattern. Increasing the number of layers will also adversely, although slightly, affect performance.
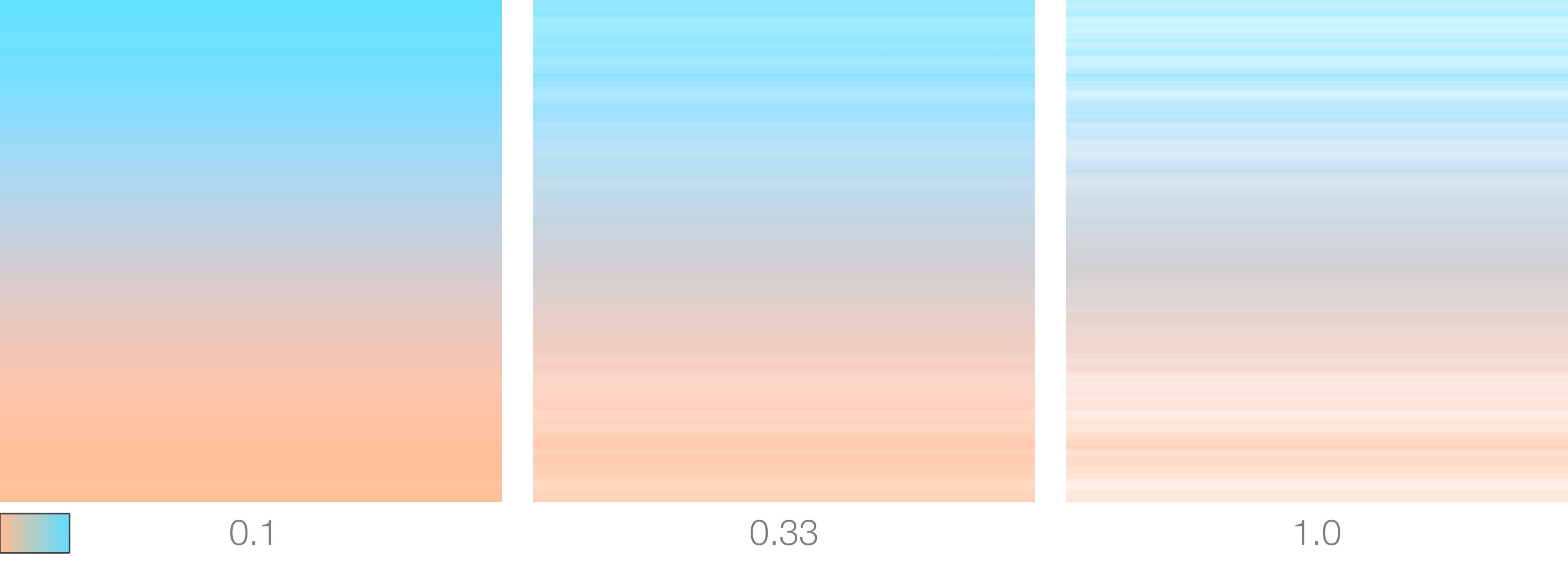
Noise Layers Persistence
The intensity of the more detailed layers, when blended with lower detail layers, is scaled by variable. The higher this value the more busy the noise will look.
Noise Layers Scale
Controls the relative detail (or frequency) of each added noise layer. Common fractal noises will add twice the detail (meaning 0.5 in Noise Layers Scale) at each level with half the intensity (meaning 0.5 in Noise Layers Persistence)