The Gobo Light Filter is a filter placed in front of a light source that tints or blocks the emitted light. Gobo light filters can be applied on spot lights or area lights.
Creating a Gobo Light Filter
To create a gobo light filter, right-click in the GafferThree's Object table and select Add → Gobo Light Filter, or press the B key. A gobo light filter is shown as a square in front of the light it is applied on in the Viewer.
A gobo filter in the Gaffer Object Table, and as a white square when applied on a spot light, in the Viewer.
Applying and Positioning a Gobo Light Filter
Applying a Light Filter to a Light
In order to apply a filter to a light, it must be set as a child of that light. Alternately, a light filter reference can be put in place as a light child; it will act as a filter proxy. To set the filter as the light child, simply middle-click and drag the light filter on the light, in the Gaffer Object Table. To use a light filter reference as a proxy: Using a light filter reference allows sharing one filter with several light sources.Alt+F;
It also permits decoupling the filter transform from the light source transform, so it becomes possible to move / rotate / scale one without the other. The next section explains how this can be achieved.
Positioning a Gobo Light Filter
Placing a gobo light filter as a child of a light will make the filter always follow the light source.
To position the gobo light filter independently from the light source:
- Make sure that the gobo light filter is not parented to any light in the Gaffer Object Table;
- Apply the filter to the desired light sources using a light filter reference, as explained in the previous section;
- Turn on the Use Filter Coordinate System on in the gobo light filter's Material tab.
The gobo light filter can now be positioned by editing its transform in its Object tab.
Controlling a Gobo Light Filter
Interactively editing Gobo Filter Controls in the Viewer
To enable the Gobo Filter Manipulator, select a gobo light filter in the Scene graph or the Viewer. It will unlock a Manipulators → Gobo Filter menu item in the Viewer. Choose this menu item or press the Tab key to display the gobo filter manipulator.
Displaying the manipulator will also fill the Quick Editor with the gobo filter parameters. The Quick Editor can be displayed by choosing Layout → Show Quick Editor, by pressing the A key, or by dragging the right edge of the Viewer to the left.
The gobo filter manipulator offers controls on the Offset and the Scale parameters. Drag the manipulator arrows to edit offsets. Drag the manipulator boxes to edit scale values. The Offset and the Scale parameters are detailed in the next sections.
The gobo filter manipulator in the Viewer.
Gobo Light Filter Controls
The object tab presents the Gobo's transform. The transform is ignored in the rendered image when Use Filter Coordinate System has been turned off in the Material tab.
The Material tab contains several parameters which are explained in the following sections.
The Object tab of a gobo filter.
The Material tab of a gobo filter.
Map An image file that is used as a filter. The image should have been processed beforehand by tdlmake. Density A map opacity multiplier. A density of 0 makes the map completely transparent.
Invert Turning this parameter on will invert the map colors. Use Filter Coordinate System Defines if the translation, rotation and scale specified in the Object Parameters will be applied to the filter. When this parameter is disabled, the light transform is used for the filter. Note that if the filter is set as a child of the light, then the light transform will always affect the filter. To dissociate the light transform from the filter transform and use only the later, please refer to Positioning a Gobo Light Filter above. Scale The scale factors applied to the range of S and T values covered by the filter, respectively. Values between 0 and 1 will appear to enlarge the map since the whole filter will cover a smaller portion of the usual texture coordinate area (from 0 to 1).
The wrap modes were set to 'periodic' for the scale illustrations. Offset Specify S and T offset values applied on the map, respectively.
The wrap modes were set to 'clamp' for the Offset illustrations. S Wrap Mode Control how the area outside the filter coverage will appear. The available options are: Coordinates below 0 are set to 0, and coordinates above 1 are set to 1. This will effectively repeat the map's border pixel. Coordinates below 0 and above 1 are mapped to a black color. The area outside the 0 to 1 range use coordinates that are repeated in a mirror fashion - from 0 to 1, then 1 to 0, and so on. The area outside the 0 to 1 range use values from 0 to 1 repeated over again.
Note that the corner pixels of the map are not black, hence the checkerboard pattern on the Clamp image.
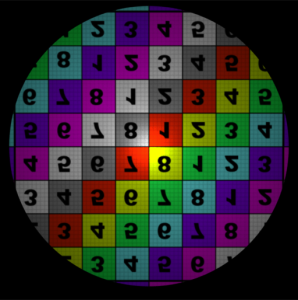


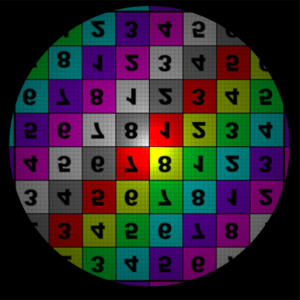
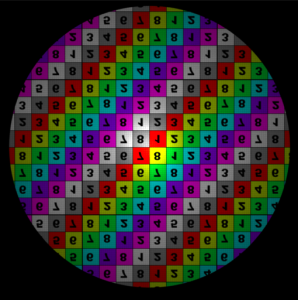
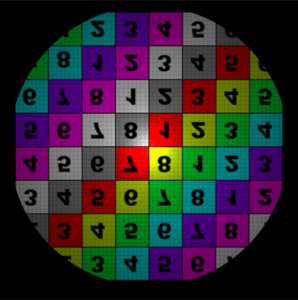
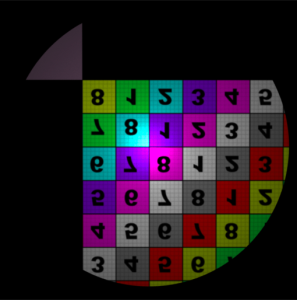
T Wrap Modeclamp
black
mirror
periodic