Introduction
Outlining features are typically used to define "silhouettes" and other geometric features in Animé-style rendering (Japanese アニメ), in illustrations and in technical drawings.
In Animé, outlines are often combined to CEL / "toon" shading, a style of non-photoreal rendering (NPR) designed to make 3D computer graphics appear to be more "flat", usually by thresholding and stepping the illumination, creating well-definied color regions. Maya "Ramp Shader" is a simple example of "toon" material and is supported by 3Delight for Maya. For more advanced Animé-style features with 3Delight we recommend to look into the Maneki solution, by J CUBE Inc.
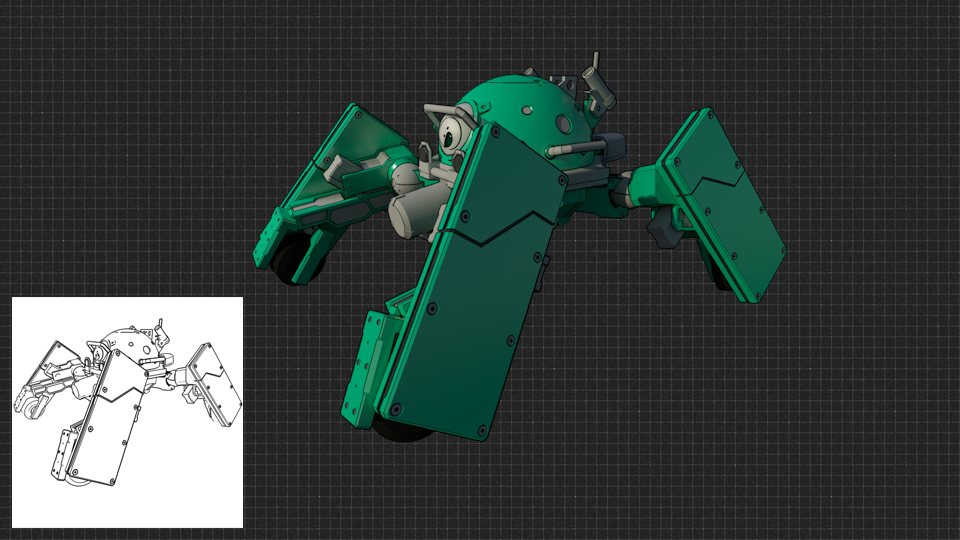
Outlines can also be combined with physically-based style rendering (PBR) to develop more hybrid, photo-surreal rendering (PSR) and artistic looks such as in Figure 1. and 2b. where outlines are combined with smooth shading, HDRI environment lighting, area lights, GI and indirect reflections.
Figure 2b. A "PSR" Maneki Neko (http://maneki.sh)
Outlining principle of in 3Delight for Maya
3Delight for Maya offers an easy to use and powerful mechanism to render outlines and allows a whole range of artistic styles.
The principle of outlining in 3Delight for Maya is simple:
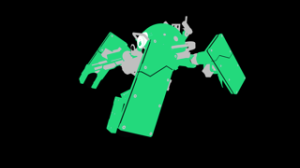
one (or more) image layer(s) can be used to generate outlines (via sub-sampled edge detection), while other layers can receive outlines (outlines are then drawn in that layer).
Typically, one layer receives outlines generated from a quantity of other layers such as as object_id, depth and normal layers to generate outlines on an RGBA layer or on a separate outline-only layer. Outlines will be therefore detected and generated around the contours of objects, between areas with sudden normal and depth variations, or other sharp geometry details differences.
3Delight for Maya offers a WYSIWIG workflow so that it is easy for artists to visually understand where outlines are generated simply by looking at the imager layers tagged as generators.
3Delight for Maya outlining relevant UI is located in the Image Layers section of the Render Settings, additionally, outlines width scaling and color can be controlled/overridden on a per-material basis using HyperShade network, such controls are available in the Maya ShadingGroup nodes.
3Delight for Maya can perform outlining on any number of Image Layers (AOVs), including:
- shading component AOVs
- auxiliary AOVs
- Multi-Masks (3delightMaskSets) AOVs
- Multi-Light AOVs
- custom AOVs (any shading variable can be used for outline detection when output as a shading output)
Furthermore 3Delight powerful layer display subsets allow to isolate the detection on specific Maya sets only.
Advantages of using the 3Delight outlining system
- Powerful, AOV-based, decoupling of the detection phase and the drawing phase
- Ability to isolate detection on a subset basis via layer display subsets and Multi-Masks AOVs
- Easy & logical to setup (WYSIWYG)
- Ultra high quality outlines, due to state of the art sub-sampling, anti-aliasing and filtering: increasing pixel samples produce beautifully anti-aliased outlines.
- Ability to use high-order filtering kernel such as since, catmull-rom, mitchell.
- Fully working both in interactive IPR and final frame (progressive) rendering.
- Outlines are drawn immediately (no need to wait for the end of the frame to see the outlines).
- Outline rendering is very fast, with virtually no additional cost.
- Strong outline stability in animation, due to 3Delight rock solid geometry pipeline and analytic tessellation of subdivisions surface and displacement
- Supported in both Path Tracing (default, scalable and higher quality) and REYES (faster, for simple scenes, but lower quality)
Can be easily combined with PBR effects for hybrid "PSR" visual results
- High-quality sub-pixel displacement of geometry and, accordingly, of its outlines.
- Complete color-managed linear workflow pipeline for both colors, textures and outlines.
Efficient, concurrent, multi-camera rendering for Stereo & VR cameras.
A simple RIB example scene can be found at this location inside your 3Delight installation: $DELIGHT/example/maya/outlines.
Outlining in the Image Layer
The Outlining subgroup
Draw Outlines in this Layer
This attribute enables drawing of outlines for the selected layer. This can be seen as an indicator of which layer receives the outline. It is set to off by default with the exception of the "outline" auxiliary AOV which receives outlines by default.
Generate Outlines Using this Layer
This attribute enables outline generation using the specified layer. Good image layers for detection purposes are the ones with sharp color discontinuities which facilitate the detection algorithm. When multiple image layers are used for generation (detection), they will be combined and drawn together and hiding will be resolved according to depth informations.
Usually (a combination of) the following auxiliary image layers, available in the AOV Selector or in custom shaders, are used to generate outlines:
- World Space Normals
- Geometry ID / Shader ID
- Depth
Technically it is possible to use any AOV/image layers, the following are available in the AOV Selector or in custom shaders, and can be used to detect and generate outlines, we provide some side by side examples here below:
| Image Layer | Detection | Generation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| surface color (auxiliary) | this is the un-shaded and un-illuminated (textured) color of any object. It offers good stability, however detection will act on any eventual texturing applied to it, this means you can use ad-hoc textures to trigger detection of any detail you might want and for the same reason this might not be the ideal choice for detection in other situations. | ||
| root ID (Maneki) | the unique color-coded root ID (supports also instances). It offers goods stability across frames/shots being purely based on the maya full object name, and will detect an outilne between different hierarchies in the Maya DG | ||
| geometry ID (Maneki) | the unique color-coded geometry ID (supports also instances).It offers goods stability across frames/shots being purely based on the maya full object name, and will detect an outilne between different object/instances in the Maya DG | ||
| shader ID (Maneki) | the unique color-coded shader/material ID. It offers goods stability across frames/shots being purely based on the maya full material name, and will detect an outilne between different materials | ||
| face ID (Maneki) | the pseudo-unique color-coded ID for each face. This offers good stability. It detects a "wireframe" for the geometry. In order to export meshes with "face ID" information you need to add delightGeoAttributes> Geometry> Polygons> Export FaceID. | ||
| depth (auxiliary) | this image layer is less stable, being view-dependent. It is often used to resolve, for example, facial features such as a jaw line. An outline will be detected between regions at different depth. Fine tuning with the outlining threshold is required. | ||
| world space normal (auxiliary) | this image layer is less stable, being view-dependent and gradient colored. An outline will be detected between regions where surface normal, in world space, face away. Fine tuning with the outlining threshold is required. Normal/Bump maps can be used to tweak geometric features and provide a correspondent detection. | ||
| camera space normal (auxiliary) | this image layer is less stable, being view-dependent and gradient colored. An outline will be detected between regions where surface normal, in camera space, face away. Fine tuning with the outlining threshold is required. Normal/Bump maps can be used to tweak geometric features and provide a correspondent detection. | ||
| facing ratio (auxiliary) | this image layer is quite stable, it features a greyscale gradient similar to what is computed for the ‘samplerInfo’ node’s ‘facingRatio’ output plug. An outline will be detected between regions where the dot product between the surface normal and the eye direction diverges. Fine tuning with the outlining threshold is required, and in general a larger-than-default threshold value is necessary for this image layer. | ||
| shadow (custom) | this offers good stability only if the shadow is sharp. Works for both delta-lights (spot/point/direct), area lights and environment. An outline will be detected around the shadow region. | ||
| curvature (Maneki) | a custom image layer that computes surface curvature based on several methods, it is pretty hard to detect stable curvature for the whole frame so it should be controlled on a shader basis, when controls are available. Fine tuning with the outlining threshold is required. In general detecting on curvature will not produce better result than detecting on normal AOVs. | ||
| multi-masks | any combination of geometry, materials or a mix of both, in a 3delightMaskSet (multi-masks): being black and white masks offer perfect contrast for detection. |
There is a wide range of artistic possibilities as any number of AOVs (including masks, auxiliary and custom ones) can be used to detect outlines, regardless of how stable they are it is up to you and your artistic purposes to define the look.
When the "generate" toggle is enabled, a part of the UI becomes sensitive to set the parameters of the outlines.
Outline parameters become sensitive for layers generating the outline.
Color
Specifies the color of the generated outline. It is set to white by default.
Outline Width
Specifies the width of the generated outline. It is set to ‘0.2’ by default. Values between ‘0’ and ‘1’ are allowed, producing very fine outlines. In this case it is recommended to raise the Pixel Samples attribute (in the Quality group or rendering attributes) in order to avoid aliasing of the outlines. Next to this attribute, there is an option menu to determine how this width should be interpreted. The available options are:
Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Pixels | The filter width is a number of pixels. This is the default. |
| % of Frame Width | The filter width is taken as a percentage of the image resolution in X. This is the recommended choice since it preserves the look of outlines at different output image resolution settings. |
Threshold
Specifies the sensitivity of the outlining. The higher the threshold the more sensitive is the edge detection. For example, when detecting variations on ‘z’ (depth), a value of ‘0.1’ means that if there is a gap of ‘0.1’ between two surfaces (in the z direction) then an outline will be generated. This attribute is set to ‘0.1’ by default.
Depth Based Fadeout
Specifies the edge thickness fadeout with depth, this is necessary in animation so that objects far away from the camera will have thinner lines. It is off by default.
Min Z
Max Z
These two attributes are scene-distance dependent and specify the depth range on which the fadeout will be performed. By default, "Min Z" is set to ‘0.0’ and ‘Max Z’ is set to ‘1000.0’. The values are in Maya default units. Usually users need to set a max Z value depending on scene size.
Min Filter Width
The depth based fadeout will keep outlines with a minimum width specified by this attribute. Its default value is ‘1.0’. Usualy there is no need to tweak this control.
Controlling Outline scale and Color
Outline scale and color are controlled globally, in the Image Layer outlining section, and for each image layer you are detecting on:
The Outlining subgroup
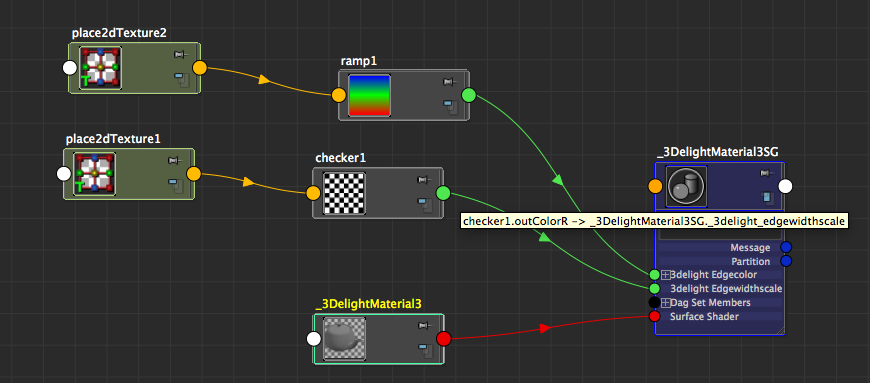
You can locally control the outline color and the outline width scale (thickness) on a per-material basis and override the global settings by mapping the relative attributes which are present in each Maya ShadingGroup nodes under the 3Delight section.
The 3Delight outlining attributes on a Maya Shading Group node
Simply connect any Maya shading node/network, keep in mind that:
- the UV coordinates used for the mapping are inherited by the geometry to which the material is applied
- the outline color is of type 'color'. This color will be used instead of the color specified in the global image layer settings.
- the outline width scale is of type `float`. This is a scaling factor ranging between 0 and 1 (meaning it cannot be larger than the value specified in the Image Layer). It will scale the width specified in the global image layer settings:
final_outline_width = image_layer_outline_width * shading_group_outline_width_scale
An example in connecting outline color and outline width scale (float edgewidthscale)